Helpful tips
Plant propagation. About cuttings or seeds
Plants can be propagated in two very different ways: generatively via seeds and vegetatively via cuttings or other plant parts (leaf, shoot or root pieces). Generative, i.e. sexual, propagation takes place via seeds. The new plants contain genetic material from both the mother plant and a father plant, and new properties and characteristics can be formed as a result of this genetic mixing; the plants are variable. In evolution, this is essential to ensure adaptation to changing living conditions and the colonization of new locations. This factor is equally important for plant breeding, as it is the only way to develop new varieties. In vegetative propagation, on the other hand, an offspring is grown from part of the parent plant. In this method, the new plant will be identical to its mother in all characteristics, since there has been no mixing of genetic material - there is no father plant. Therefore, it is also called asexual reproduction. This is the method of choice, for example, when valuable varieties are to be preserved, and has the advantage that the development of plants propagated in this way is usually faster and they flower or fruit earlier.
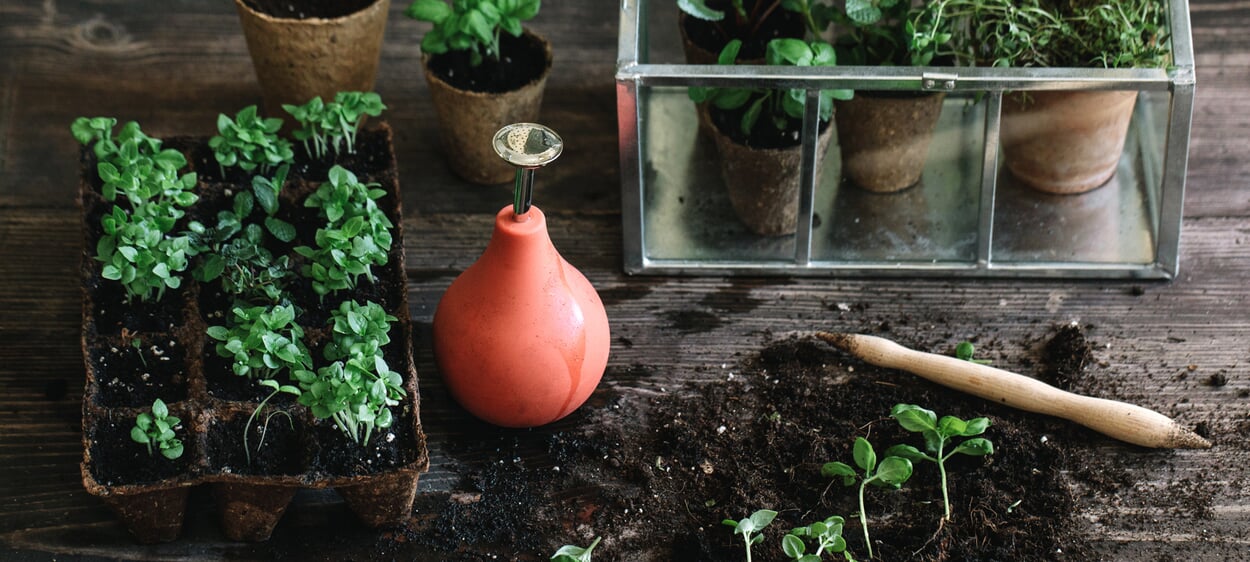
Plant propagation at home
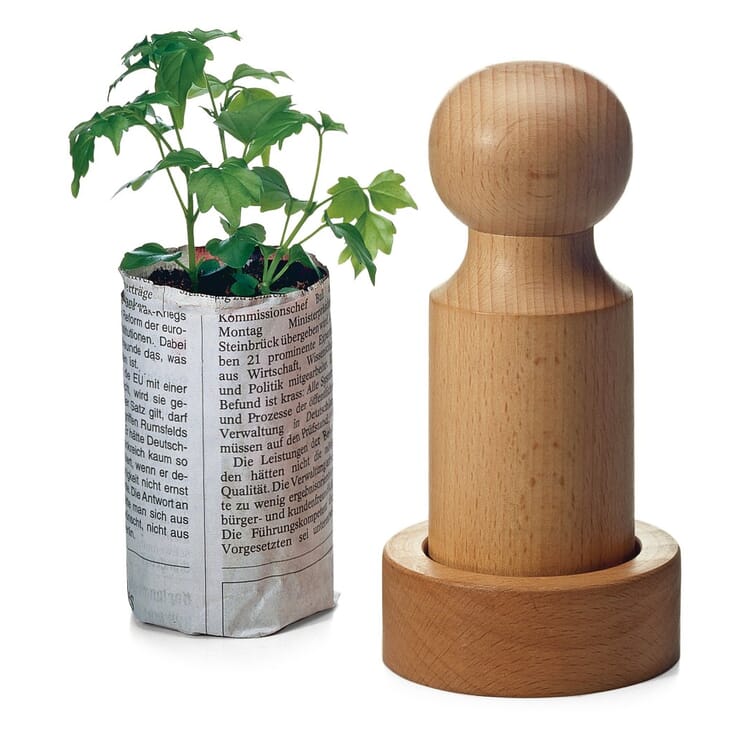
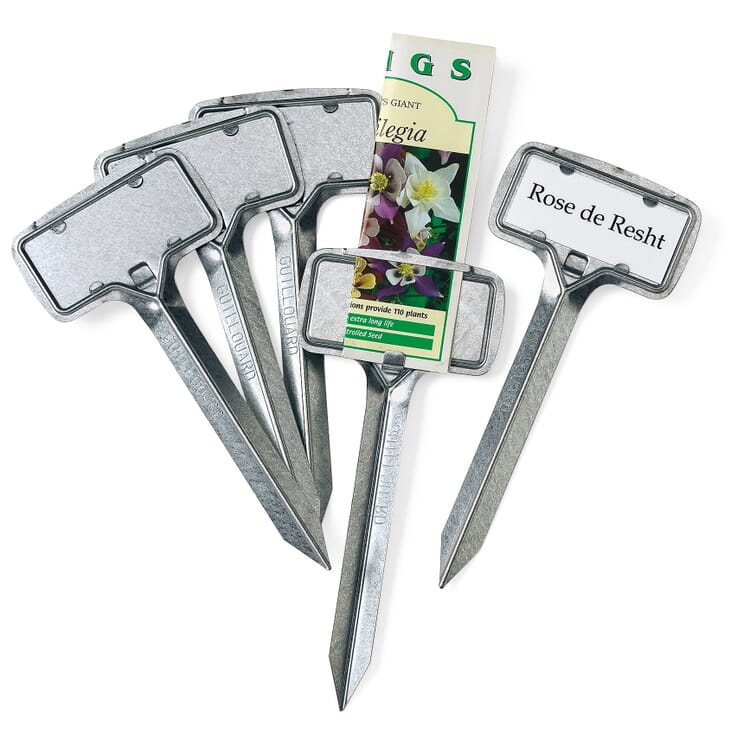
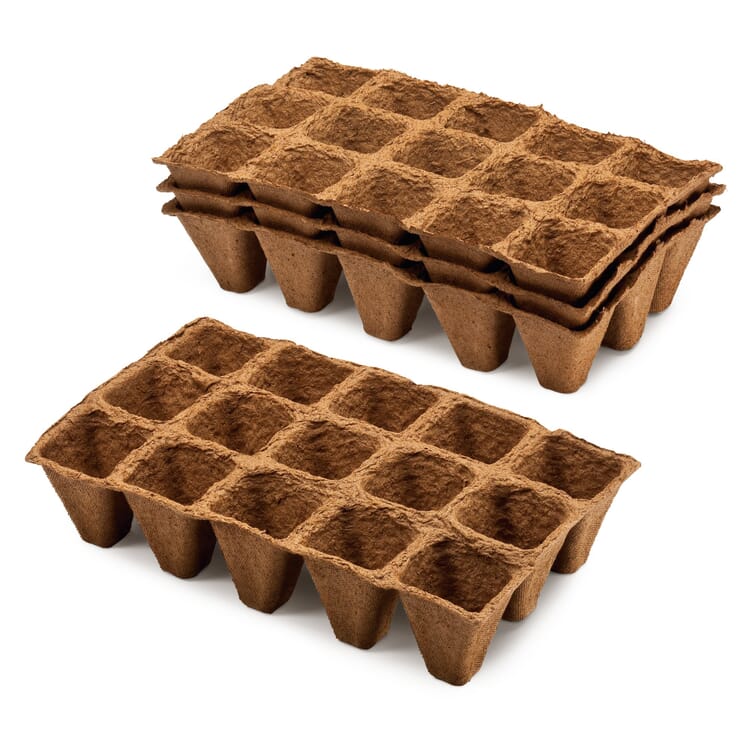
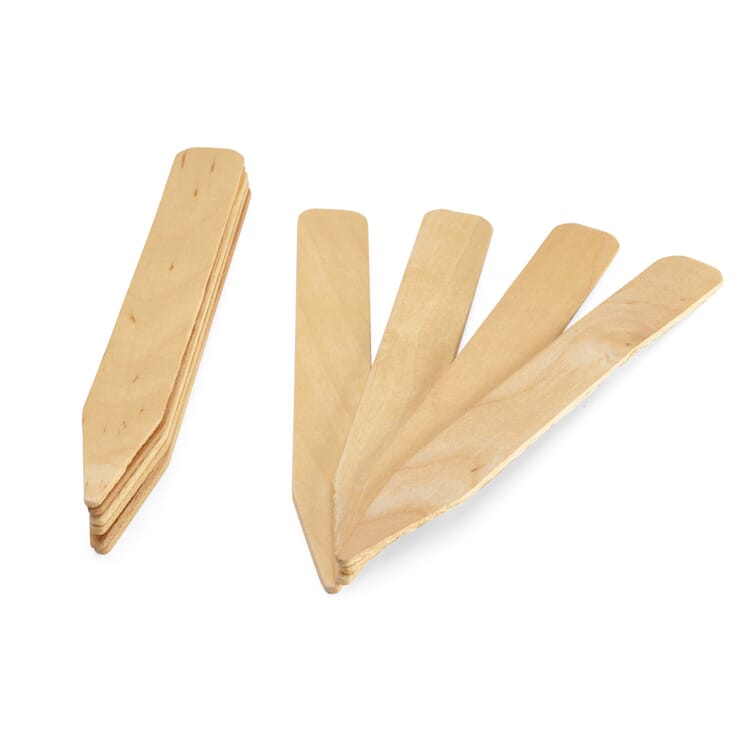
However, other factors are usually decisive for the choice of cultivation method in amateur gardening. In the spring, plant cultivation in our latitudes must take place indoors (the so-called pre-growing), and those who do not have a greenhouse, have to cope with cramped space on the windowsill. Sowing in this case has the advantage that seedlings take up less space and can be accommodated in greater numbers. In summer, plant propagation can also take place outside and herbs or balcony plants can be propagated with the help of cuttings. In addition to a greenhouse or cold frame, the necessary utensils include pricking out wood, a sieve, propagation containers and labels, as well as suitable source pots or (germ-free and low-nutrient) soil.
Potting soil. Choose alternatives to peat
When choosing a potting soil, it is important to consider one important criterion. Although in professional conventional horticulture - despite the immense disadvantages for the environment - continues to rely on peat substrates and peat swell pots, it is now easy for the amateur gardener to get good quality alternatives that work: Soils made from coconut and wood fibers, humus and compost are available, and growing utensils are made from pressed wood, paper or coconut fibers.