Medicinal plants A|B|C
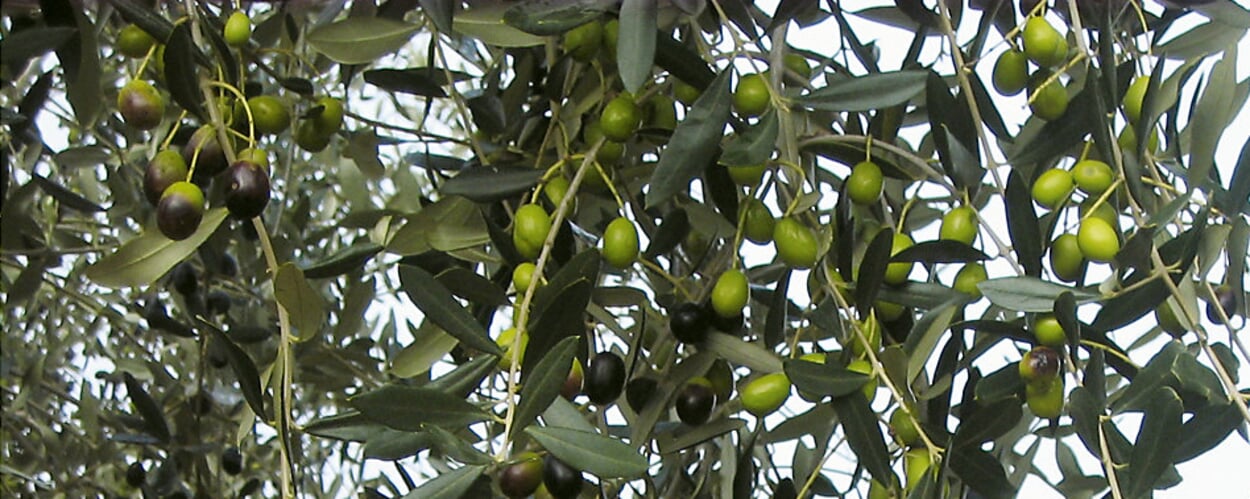
Olive Tree (Olea europaeus)
The evergreen oil tree grows up to 20 meters high and tolerates drought, the more sun it gets the better. It is easily recognized by its bizarre growth forms and silvery green leaves. It is also famous for its longevity. The oldest known specimen is on Crete, its age is estimated at 3,250 years - and it still bears fruit. Since the 2004 Olympic Games in Athens, the winners of the marathon races have been honored with a branch of this unique olive tree.
Origin and cultivation.
The smaller wild form of the olive tree is native to the Mediterranean region and the Middle East, but also to South Africa. It has been cultivated as a source of oil since 4,000 BC, and today there are over a thousand varieties. The olive tree feels most at home in the vicinity of its own kind - it does not get along well with other tree species. The most important olive oil producing countries are Spain, Greece, Italy and Turkey. However, traders and consumers have to be careful: The amount of "extra virgin olive oil" produced worldwide is many times less than the amount sold in stores under this declaration.
Ingredients.
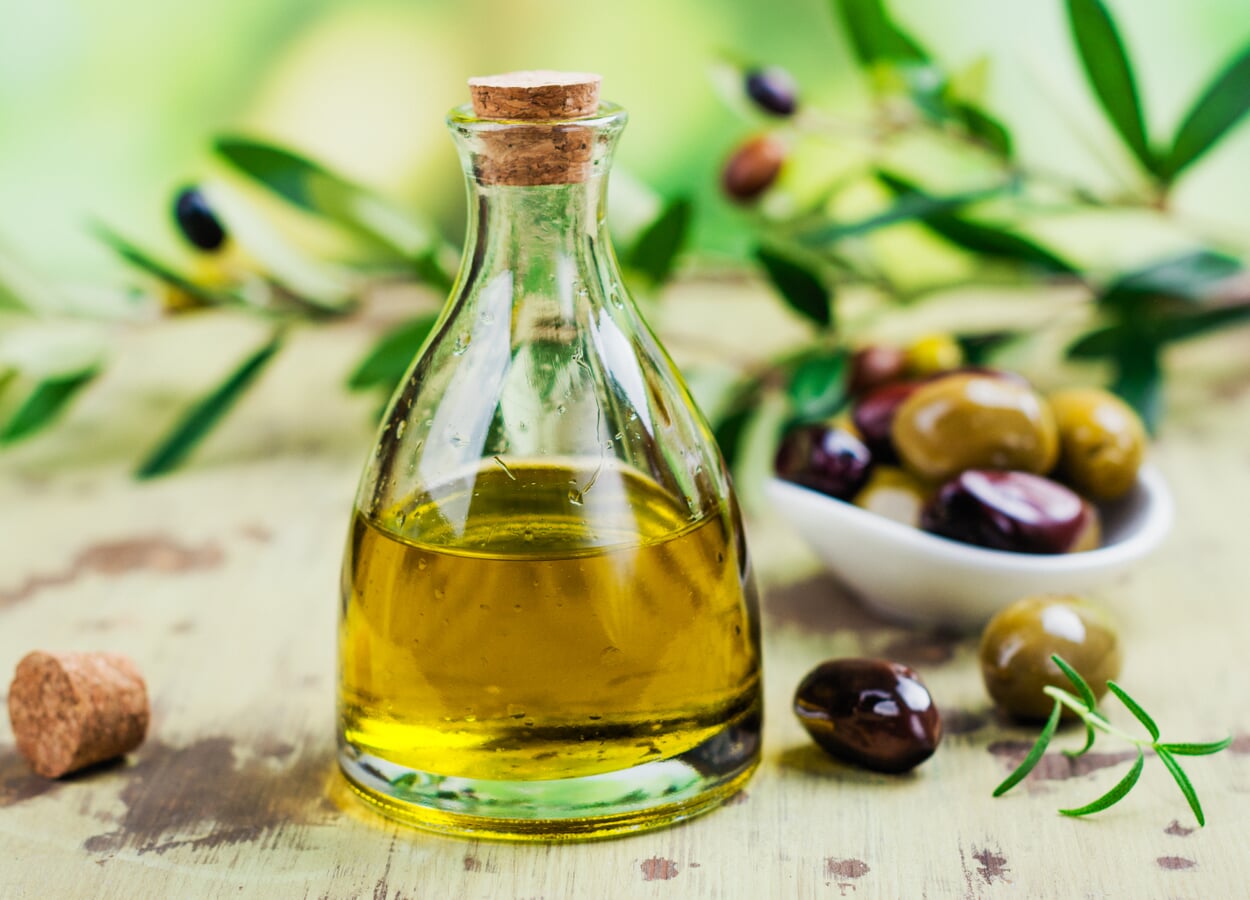
Olives are inedible straight from the tree; their bitter substances must first be flushed out by careful pickling in brine. Unlike many other oil fruits, the oil is not extracted from the pit but from the pulp; ripe olives contain about 50 percent water and 22 percent oil. Olive oil's high content of unsaturated fatty acids makes it particularly valuable for health. However, oleocanthal (its anti-inflammatory effect is comparable to that of ibuprofen) and the antioxidant polyphenols are only present in cold-pressed oil.
Products with olive oil
Use of the olive tree.
- For body care, olive oil is popular as a base for many medicinal herbal oils, ointments, soaps, masks and hair care products, because it is particularly easy to emulsify and is well absorbed by the skin. The contained linoleic acid provides moisture and protects against dehydration.
- Olive oil is used as a liniment for muscle and joint pain and internally to stimulate bile activity and treat constipation.
- The leaves of the olive tree collected in spring are prepared as a tea or extract and have antipyretic, diuretic and antispasmodic effects.
Olive pits contain substances that gradually break down the valuable secondary ingredients of olive oil. Therefore, if the olives are pitted before pressing, the nutritional value is higher and the oil also has a much longer shelf life.
Exclusive Manufactum body care products
Recommended Topics
The citrus-scented lemon balm shrub grows up to 80 centimeters high and 30 years old. Once the lemon balm has found a sunny, wind-protected spot in the garden, it reliably sprouts again and again and forms small white lipped flowers from June to August. Its name is well chosen, because Melissa is "honey bee" in Greek; in ancient times the plant was cultivated as a pasture for bees, and today's beekeepers prevent their bee colonies from swarming by rubbing the hive with lemon balm leaves.
View moreThe gnarled and with pointed thorns provided myrrh belongs to the balsam family and grows in shrub or tree form. It grows only a few meters high and is well adapted to the dry scrubland of its homeland: Its leaves are very small and appear just before the beginning of the rainy season, together with the pendulous flower panicles. The smooth and thin bark is cracked and flakes off in small shreds.
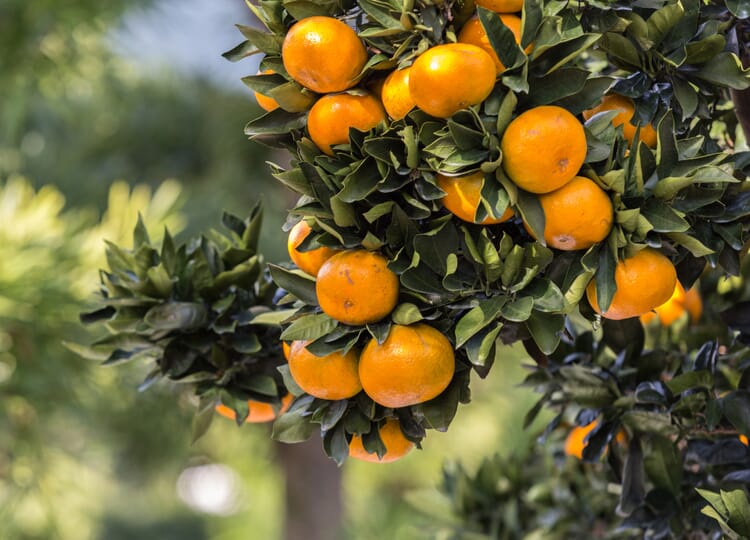
View moreThe orange trees grow up to 10 meters high with a short trunk and compact crown. They produce flowers and fruits at the same time - the combination of the dark green foliage, the small white flowers, which are fragrant for a long way, and the bright orange fruits is particularly attractive. The green fruits turn vivid orange only when night temperatures drop below 17 °C.
View more